16 December 2024
When we think of sports, we often picture the heart-pounding excitement of the game, the roar of the crowd, and the thrill of victory. But for some, the buzz isn't just about the game itself. There's another, darker side to the world of sports that has nothing to do with touchdowns, goals, or home runs. I'm talking about hooliganism – a chaotic, sometimes violent, subculture that lives on the fringes of sports.
From street fights to stadium brawls, hooligans are often more interested in clashing with rival fans than watching the game. It's a world fueled by adrenaline, loyalty, and sometimes outright mayhem. So, what exactly is hooliganism, and why does it still have a grip on certain corners of the sports world? Let’s take a closer look at this extreme phenomenon.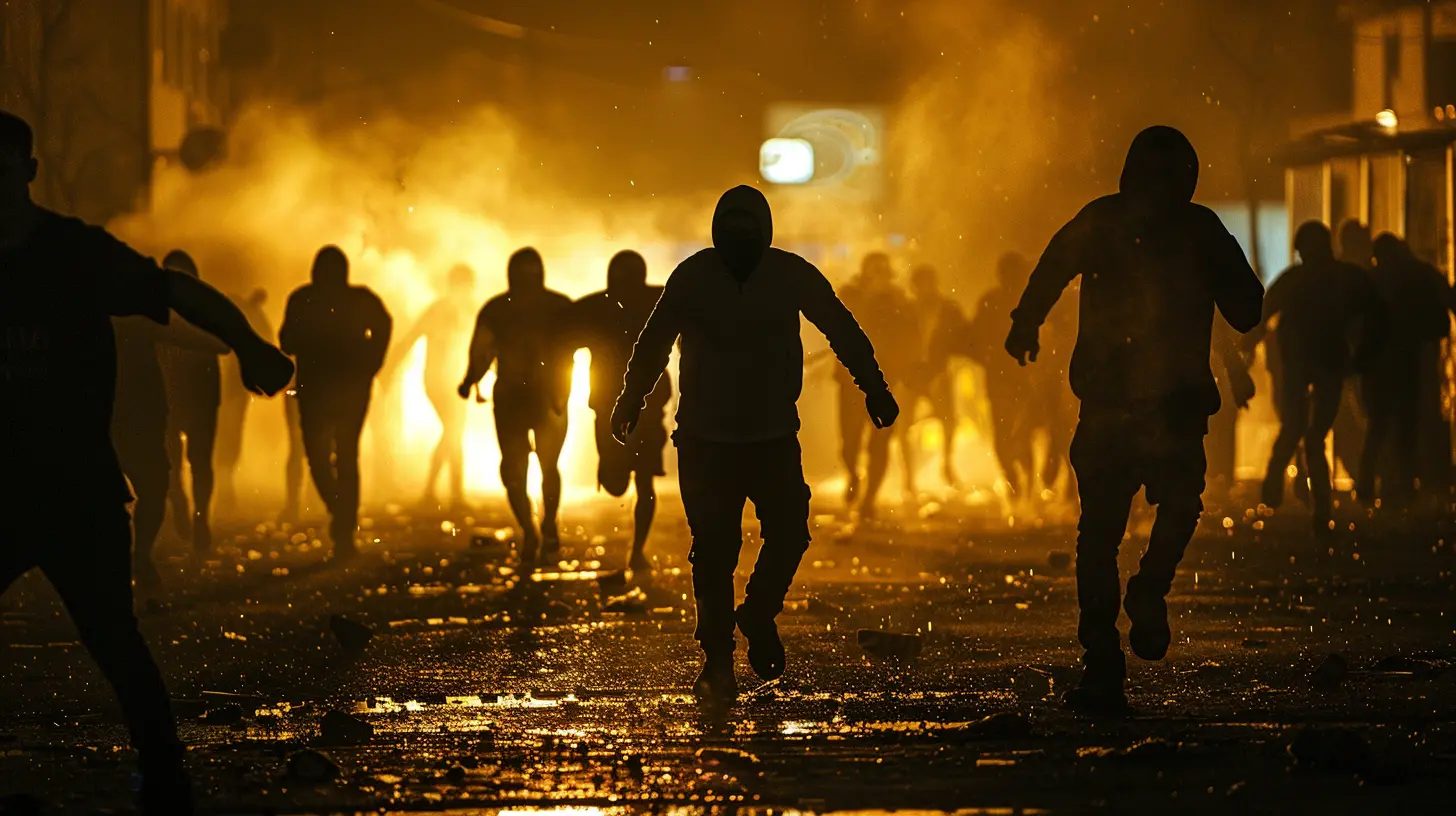
What Is Hooliganism?
Hooliganism is essentially a form of aggressive, unruly, and sometimes violent behavior associated with sports fans. It's been around for decades, and while some may think of it as a relic of the past, the truth is that it’s still alive and kicking today.Think of it as the darker cousin of fandom. While most sports fans are content with cheering for their team, wearing the colors, and maybe talking a little smack to their rivals, hooligans take it to the next level. They form organized groups, known as "firms" or "ultras," that are dedicated not only to supporting their team but also to engaging in physical altercations with rival fans.
Hooliganism is most commonly associated with football (soccer, for those in the U.S.), but it can crop up in other sports as well. These groups often coordinate their activities, planning fights ahead of time or showing up at matches specifically looking for trouble.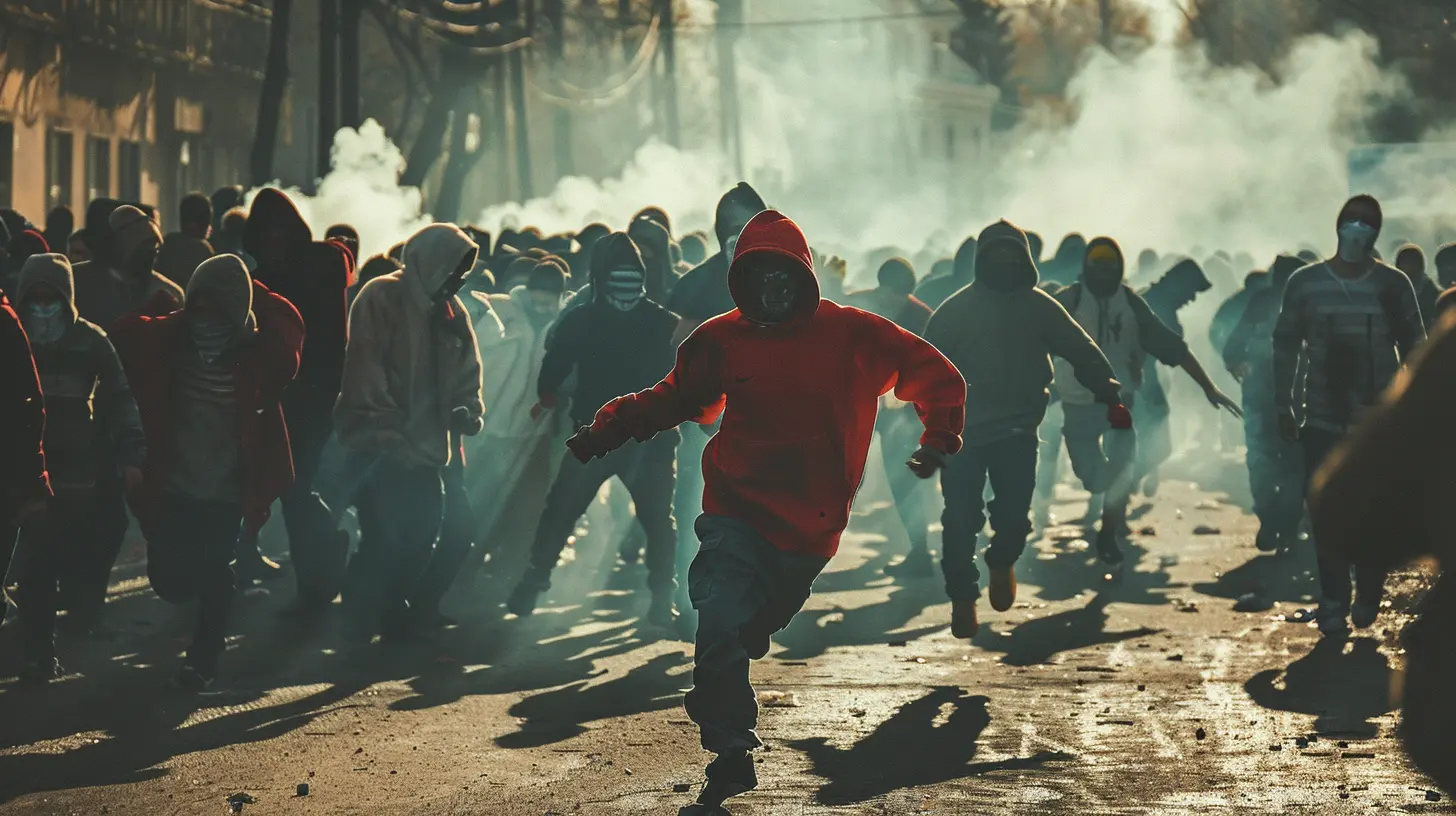
The Origins of Hooliganism
To understand where hooliganism comes from, we need to travel back in time. Hooliganism, particularly in football, can be traced back to the late 19th and early 20th centuries in England. Although sporting rivalries have existed for centuries, the modern concept of the "football hooligan" really took shape post-World War II.During this period, football was becoming a working-class sport in Britain, and with that, rivalries between teams became more intense. As teams represented different neighborhoods or even different social classes, fan clashes became more frequent. By the 1970s and 80s, hooliganism was rampant, with groups of fans deliberately arranging fights before, during, or after matches.
Interestingly, while hooliganism started in the UK, it didn't take long for it to spread across Europe and even to other parts of the world. Today, hooliganism is a global phenomenon, with infamous groups from countries like Italy, Russia, Turkey, Brazil, and many others.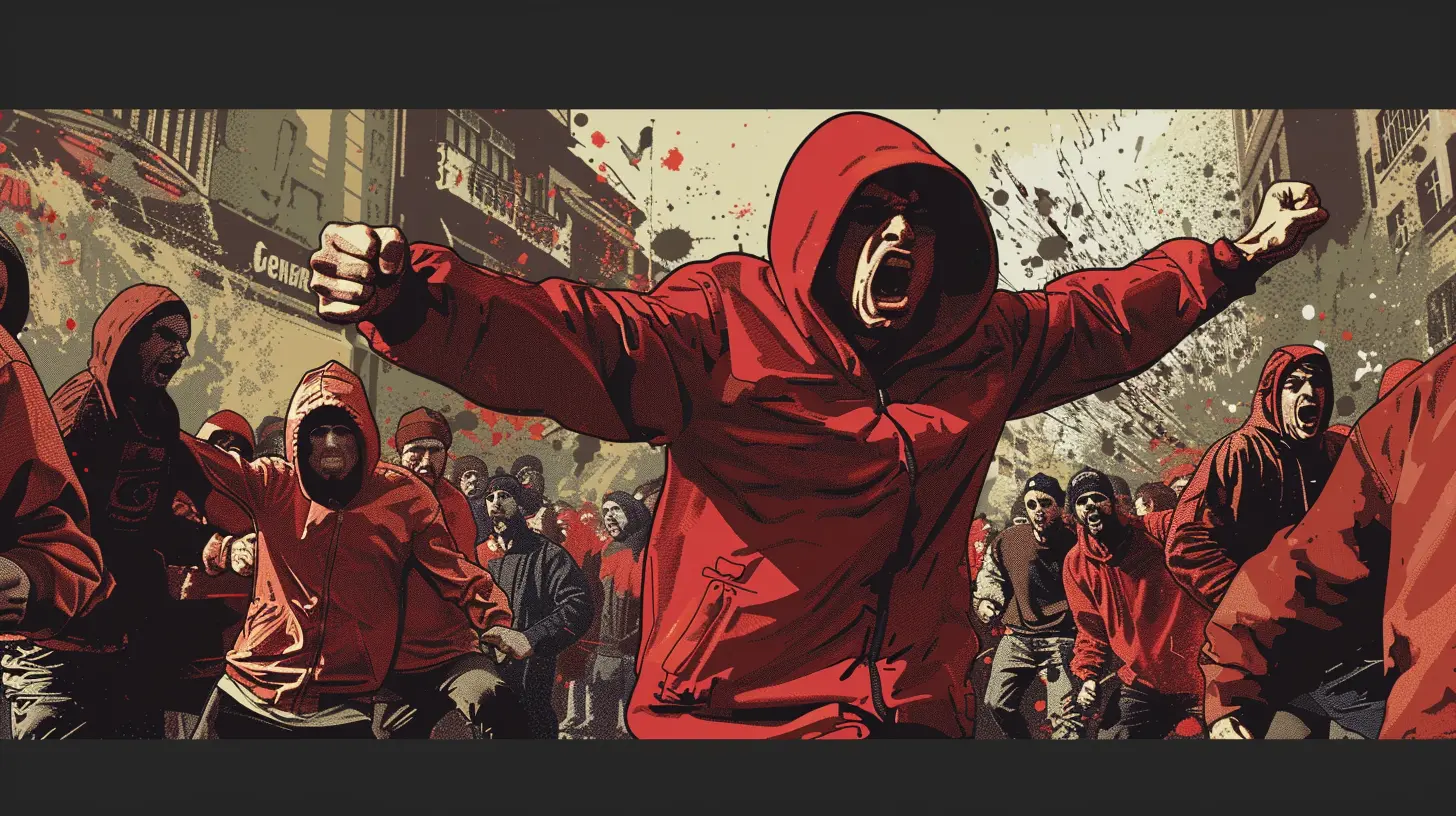
Stadium Brawls: A Clash of Pride and Territory
When you think of hooliganism, one of the first images that might come to mind is a brawl in the stands during a game. Stadium brawls are the result of tensions boiling over, often between rival fans who are seated too close to one another. These clashes can start with a simple insult or taunt and quickly escalate into full-blown fights, with fists flying and seats being torn out and used as weapons.Why does this happen? It’s often about pride and territory. For many hooligans, their team isn't just a sports club – it represents their identity, their city, and sometimes even their social class or political beliefs. When a rival fan disrespects their team, they take it personally. And once one person throws a punch, it’s like an avalanche that can't be stopped.
The authorities have tried to curb stadium violence for years with everything from increased police presence to segregating fans. But despite these efforts, stadium brawls still occur, often in high-profile matches with long-standing rivalries.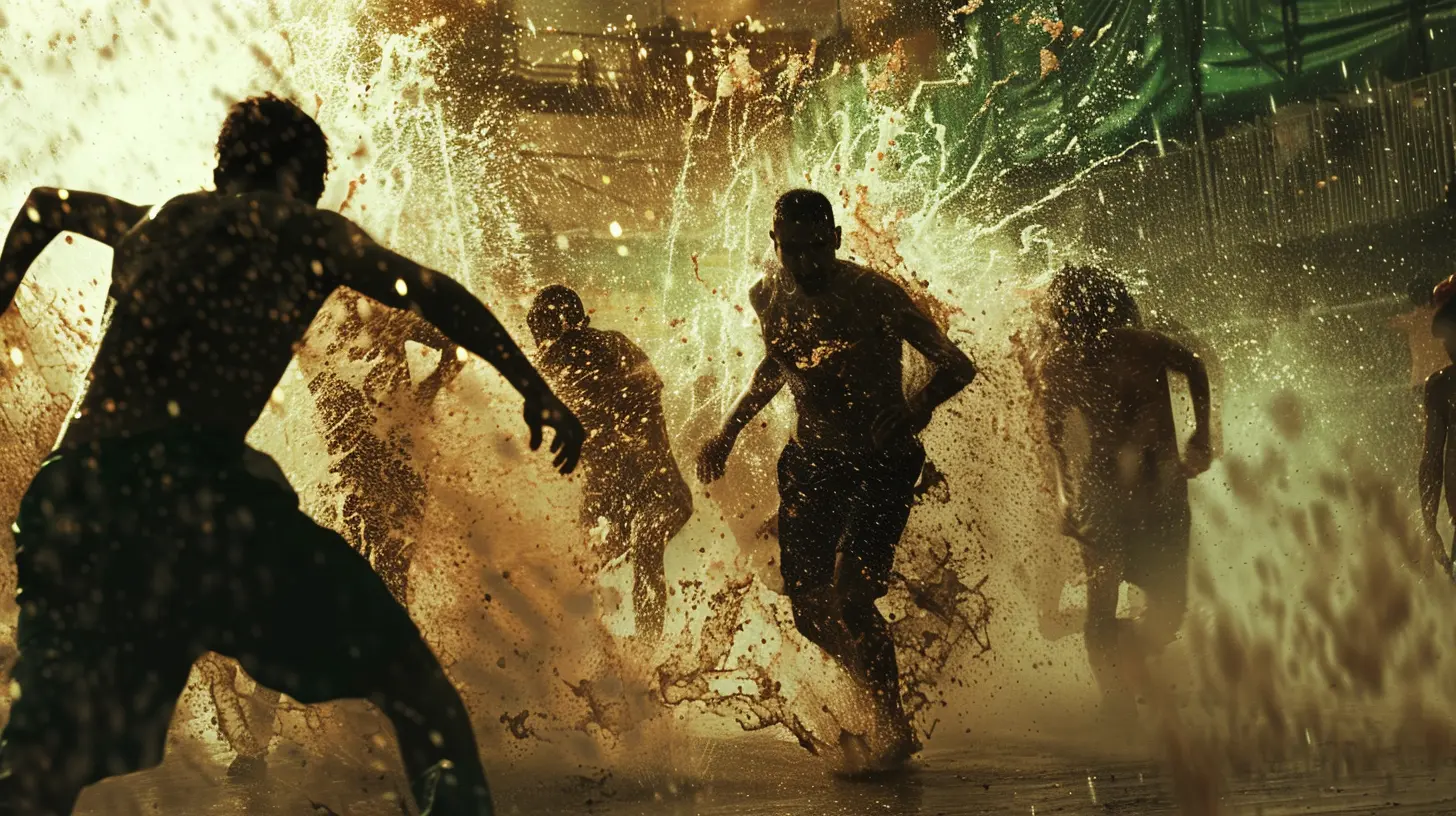
Street Fights: Pre-Planned Chaos
While stadium brawls may happen in the heat of the moment, many hooligans prefer a more organized form of chaos – street fights.These fights are often pre-planned, with rival hooligan firms agreeing to meet up at a specific location away from the stadium (and away from police) to settle their differences. These aren’t random scuffles between a few drunk fans; they’re organized brawls, sometimes involving dozens or even hundreds of people.
In some cases, these fights are even treated like a twisted form of sport. There are unspoken rules – no weapons, for example – and the goal is to prove who’s tougher, rather than to actually injure or kill. Of course, things don’t always go according to plan, and serious injuries (and even deaths) can result from these confrontations.
For many hooligans, these street fights are seen as a way to defend their team’s honor. Winning a fight against a rival firm is a badge of pride, something they can boast about for years to come. It’s as if the battle off the field is just as important as the one on it.
Hooliganism’s Global Reach
England may be the birthplace of hooliganism, but it’s far from the only country where this phenomenon exists. Across the globe, hooliganism has taken root in countless sports communities, with each country developing its own unique style of rowdy fan behavior.Italy
In Italy, hooliganism is intertwined with the country’s "ultras" culture. These fan groups are highly organized and often have connections to political movements. The rivalry between Italian clubs, such as the fierce clashes between AS Roma and Lazio, has led to some of the most notorious incidents of hooligan violence in football history.Russia
Russian hooligans have gained notoriety in recent years for their brutal, organized street fights. Russian firms are known for their physical fitness and military-like discipline, often engaging in pre-arranged fights with rival groups from other countries. The violence here is often more extreme and dangerous than in other parts of the world.Turkey
Turkey’s football rivalries are some of the fiercest in the world, and hooliganism is a major problem in the country. Matches between Istanbul's "Big Three" – Galatasaray, Fenerbahçe, and Beşiktaş – are often marred by violence, both inside and outside the stadium. Some of the most violent incidents in modern football have occurred in Turkey, with fans throwing flares, fireworks, and even knives onto the pitch.South America
In South America, particularly in countries like Brazil and Argentina, hooliganism is deeply entrenched in football culture. The rivalry between Argentina’s Boca Juniors and River Plate, known as the "Superclásico," is one of the most violent in the world. Here, hooligans are known as "barras bravas," and their influence extends far beyond the stadium, often involving organized crime and political corruption.Why Do People Become Hooligans?
It’s easy to dismiss hooligans as just a bunch of angry, violent people. But the reality is more complicated. Many hooligans are drawn to this lifestyle because of a sense of belonging. Being part of a "firm" offers a sense of camaraderie, identity, and purpose – all things that can be lacking in other areas of their lives.In some cases, hooliganism can also be a way to escape personal struggles. For young men growing up in tough neighborhoods or dealing with economic hardship, joining a hooligan firm can provide a sense of empowerment and control. The adrenaline rush of a fight, the feeling of loyalty to a group, and the thrill of danger can be addictive.
Of course, this doesn’t excuse the behavior, but it does help explain why hooliganism continues to thrive, even in societies where it’s heavily policed.
The Consequences of Hooliganism
Hooliganism is not without its consequences – both for the individuals involved and for the sports they claim to support. For one, hooligans often face serious legal repercussions. Arrests at matches or after organized fights are common, and some hooligans serve lengthy prison sentences for their involvement in violent incidents.Then there’s the impact on the sport itself. Hooliganism tarnishes the reputation of football and other sports, leading to stricter regulations, increased policing, and sometimes even the cancellation of matches. Fans who just want to enjoy the game are often caught in the crossfire, and the violence can deter families and casual fans from attending games altogether.
In some cases, hooliganism has even led to tragic deaths, with innocent bystanders or rival fans losing their lives in clashes gone too far.
Can Hooliganism Be Stopped?
So, what can be done to stop hooliganism? Authorities have tried everything from banning known hooligans from stadiums to increasing security at matches, but these measures have only been partially successful.For many, the answer lies in addressing the root causes of hooliganism, such as poverty, social inequality, and lack of opportunities for young people. By providing individuals with better alternatives, the hope is that they’ll be less likely to turn to violence as a form of expression.
Another potential solution is to focus on educating fans, particularly younger ones, about the dangers and consequences of hooliganism. Encouraging a culture of respect and sportsmanship could help curb the violent tendencies of certain fan groups.
Conclusion
Hooliganism is a complicated and deeply rooted phenomenon that goes far beyond a simple love of sports. For some, it’s about pride, identity, and rivalry. For others, it's a way to cope with deeper societal issues. But at the end of the day, the violence and chaos that come with hooliganism only serve to damage the sports that so many people love.While it may never be fully eradicated, understanding the motivations behind hooliganism and working to address its underlying causes could be the key to reducing its impact on the world of sports. After all, sports should be about unity, not division – and there’s no place for violence in the game.












Harlow Blevins
Who knew the line between sportsmanship and street mayhem was so thin? Hooligans: the only group that can turn a friendly match into a chaotic flash mob while somehow still having a taste for nachos. Just don’t ask them to share their spicy salsa!
February 11, 2025 at 5:26 AM